
Did you know Google Shopping listings are free for most merchants to use?
Google has also dropped commissions for its Buy on Google program. This means nearly any retailer can sign up for Google Shopping Actions and link their products without paying the 12% commission Google formerly collected on each sale.
Retailers and advertisers have a unique opportunity to get incredible exposure for their products. Almost half of users turn to Google to find or discover new products. This means even small businesses can put themselves in front of millions of new potential customers with just a few clicks.
What Is Google Shopping Actions?
Google Shopping Actions partners with several retailers to create a shopping experience in direct competition with Amazon. Today, this program allows retailers to upload products that appear in organic search across Google platforms. In turn, shoppers can find, compare, and buy products without ever having to leave Google.
The user-facing side is called “Google Shopping.” When a user searches for a product, it places relevant items in the Shopping tab of their results page, alongside a number of options regarding how to buy them. It gives customers access to a universal shopping cart, shareable lists, and instant checkout with saved payment credentials.
So if you burn a pan while you’re cooking, you can use Google Home to buy a new one, add it to your shopping cart to buy later, or browse and compare new pans on your phone and buy it immediately.
Just like Amazon, when users start using Google Shopping for purchases, they’ll begin seeing personalized recommendations across platforms.
It all makes for a seamless shopping experience that may increase conversions and decrease abandoned carts.
Note: Google Shopping Actions isn’t the same as Google Shopping Ads. Retailers pay for their results to appear as featured Google Shopping Ads, while organic Shopping Actions are free. The organic search element makes it different from Google Shopping Ads, where retailers pay for placement.
What Does the Order Process Look Like on Google Shopping Actions?
Let’s go back to the burnt skillet example to walk through the customer buying process. After you enter “skillet” and get a results page, click on the “Shopping” tab at the top of the first SERP. You’ll get a list of skillet options, as well as filters on the left to narrow your search.
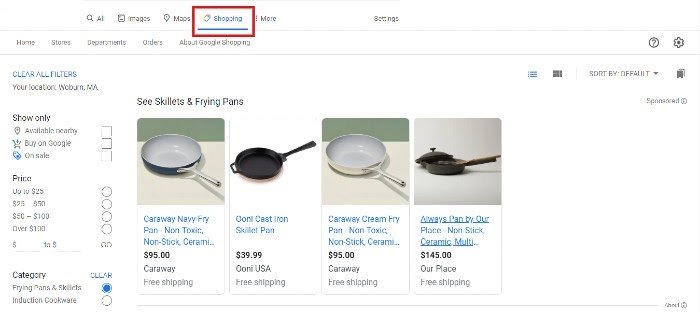
If you choose “Buy on Google,” you’ll only get options you can buy directly from Google. You’ll know which ones are part of the Buy on Google Program by the little shopping cart icon at the top left of each result:
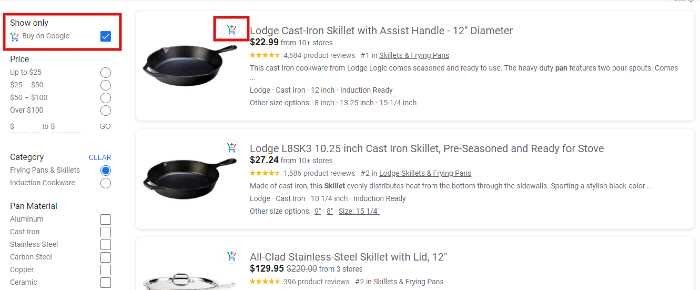
Let’s say you chose to look at this Lodge skillet that ships from Target. You’ll see product descriptions and reviews, plus the average price of similar items to help you compare.
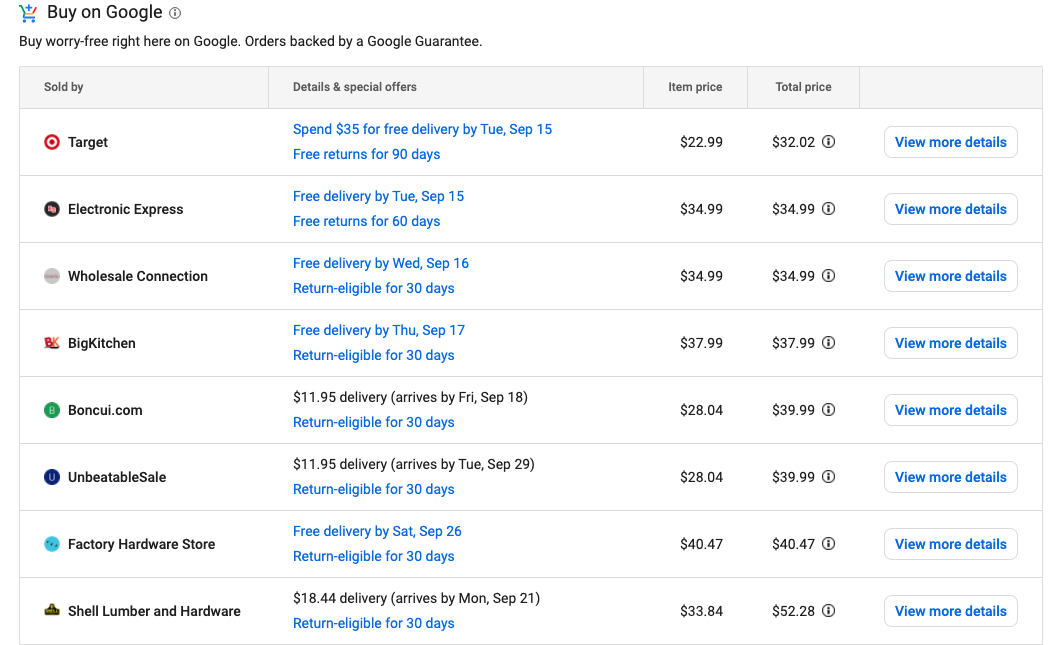
If this is what you want to purchase, you can add the item to your cart or buy it instantly.
You never had to go to the Target site, and you never had to search multiple sites to compare.
How to Get Started With Google Shopping Actions
The Google Merchant Center and Google Shopping Actions are very flexible. You can connect third-party platforms you’re already using, such as Shopify and SureDone, and even link your Amazon feed, to reduce work redundancy.
To set up Shopping Actions, you first need to sign up for a free account on Google’s Merchant Center. It’s basically your Google Shopping dashboard. You then select Shopping Actions as part of the Merchant Center sign-up process.
Once you’re signed up, you will be prompted to do the following:
- List products
- Add branding
- Select tax and shipping preferences
- Choose return preferences
- Establish user roles
- Provide customer service contact information
- Decide whether customers will be invited to sign up for a newsletter at checkout
- Include promotional information
That last one is optional, but Google recommends running promotions to attract more customers.
In order to use Google Shopping Actions, you have to implement the Orders API. This allows you to use the Google Merchant Center to manage your orders.
Of course, one of the really attractive features of Google Shopping Actions is you don’t have to manage your orders yourself. Google can handle shipping and returns and provide customer service if you choose. It’s entirely up to you.
Once a user purchases something through Google Shopping, the order shows up in your API as “in progress” for about 30 minutes. This half-hour window allows shoppers to cancel all or part of their order, if they need to. Google recommends you don’t ship anything until the status changes to “Pending Shipment.”
Things to Look Out for With Google Shopping Actions
First of all, it’s important to note that free Google shopping listings are for organic search only. If you want to place your products on specific SERPs, you have to pay through Google’s Shopping Ads program.
If you’re running Google Ads already, it’s worth setting up those same products in Google Shopping Actions, too. That way, you’re getting double the exposure for the same price.
Additionally, Google Shopping Actions is currently only available in the U.S. and France. If you’re going to sign up, you have to be a legally registered business in one of those countries and accept payment, make deliveries, and handle returns in those places.
Google Shopping Actions policies also include the following:
- Your Inventory can’t include restricted products and services. A list is available through Google Support.
- You need a valid ID from the country where your business is registered.
- You must meet all of Google’s returns and customer support standards.
Listing Your Products on Google Shopping Actions
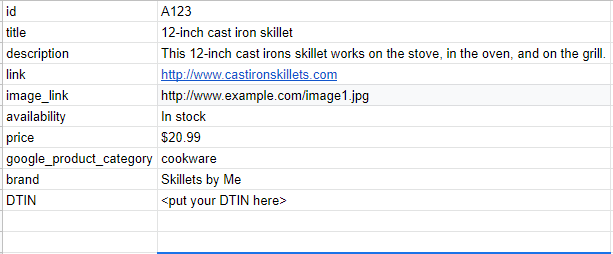
To get your products listed on Google Shopping, you have to set up a product feed. For your product feed, Google needs the following information:
- A product ID number (id)
- Product title, such as cast iron pan (title)
- A product description (description)
- A link to your product page (link)
- A link to your image (image_link)
- Product availability (availability)
- Product price (price)
- Google product category, such as kitchenware or cooking (google_product_category)
- Product brand name (brand)
- Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)
Google can crawl your site if you already have this information set up, or you can do a fetch from your servers. If you don’t have this information set up, you can create a Google Sheet or Excel spreadsheet to upload to your merchant account. Use the names in the parentheses to label your categories.
A very basic product data spreadsheet would look something like this:
Now, this information is for your primary feed. You can set up supplemental feeds as well, which can cover sales, limited edition products, or special offers.
Optimizing Your Google Shopping Listings
Like you would for your site, you want to make sure your listings are optimized for organic search.
First of all, make sure all of your information is accurate, from your description to your price. If appropriate, use geotags to make sure you pop up in local searches.
Verify your title, description, and images are optimized, as well.
Product Titles
Use strong keywords that reflect user search queries in your title. Do keyword research to see what users are searching for when they look for products similar to yours. You can use a keyword tool or simply look at the “People also ask” and “Searches related to” sections of a Google results page.
Remember, using strong keywords in your product title not only lets users find you, but it also helps Google place your products on the right results pages. Google crawls both product titles and descriptions for detailed keywords to place products.
So, instead of using “skillet” alone as your title, try something more detailed, such as “12-inch cast iron skillet.”
Product Descriptions
Make your product descriptions detailed and pragmatic. Phrases such as “amazing skillet” aren’t going to win you any organic search points. But, “Our 12-inch cast-iron skillet is seasoned with olive oil and holds heat well” tells both the user and Google precisely what your product is.
Remember to keep it short and sweet. Only 70 words show up on product pages in Google.
Product Images
According to a Weebly survey, 75% of online shoppers said product images are very influential in their decision process. That means your images should make your products look as appealing as possible.
Images should be clear, well-lit, and professional. And your products should be front and center.
Choose multiple images that give your product scale, display it from different angles, and show it in use so users can get a sense of how it will work for them.
For the cast iron skillet, Lodge shows their product served up with chicken and sizzling away on a grill with vegetables.
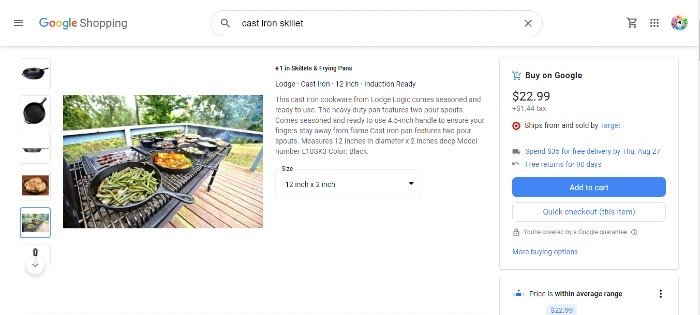
Monitor Your Product Listings
Finally, keep a constant eye on your product listings. Compare them to similar listings that are doing well to determine how to improve your own. Watch for rises or dips in visibility and clicks to see if you can attribute them to search trends.
Keep abreast of Google’s algorithm changes. A change in the way Google places organic search content could affect your listings.
What’s Changing With Google Shopping Actions?
Aside from free listings and no commissions, Google is making a few other changes to the Google Shopping experience:
- Starting with PayPal, Google is now allowing direct linking of merchants’ payment accounts to Google Merchant Center.
- Merchants can handle customer service directly, but they still have Google customer service to back them up.
- Google allows merchants to handle their own returns or choose to let Google manage them.
- The Google Merchant Center is compatible with your Amazon feed.
Google Shopping Actions vs. Amazon
Amazon is still the leader in online shopping. But, Google is beginning to give the e-commerce giant a run for its money, particularly now that listings are free. Google has a few other advantages over Amazon as well.
To begin with, unlike Amazon, Google gives shoppers more than one buying option for products. They can buy from a retailer’s site or from their brick-and-mortar locations. Many products are even available to buy right through Google.
Because Google Shopping is available across all of its platforms, users can browse shopping results and add products to their universal shopping cart wherever they are, even YouTube:
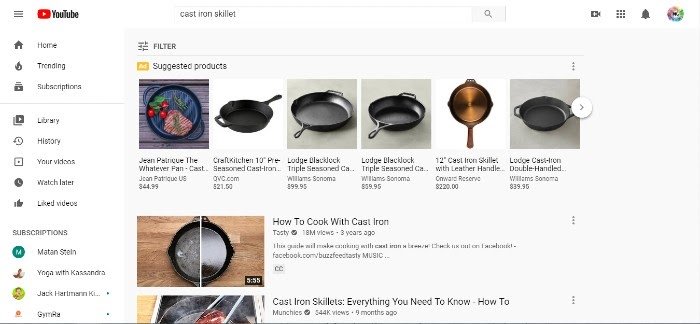
Google Shopping Actions gives you access to customer data, where Amazon doesn’t. You can track purchasing habits and trends to build stronger relationships with your customers.
Now that you can upload your Amazon feed to Google Merchant Center, it’s easier to run both programs for your products, potentially doubling their exposure.
Conclusion
With free Google Shopping, merchants have an incredible opportunity to increase their revenue through e-commerce. By optimizing your product listings through Google Shopping Actions, you can get your products in front of users and potentially help increase your conversions.
Consider running paid campaigns or just utilizing the free listings to grow your customer base and allow users to compare prices.
Have you tried Google Shopping Actions for your e-commerce store?
The post Google Shopping Actions: How to Increase Product Visibility for Free appeared first on Neil Patel.



Recent Comments